Students at the O’Connor Music Studio know that music theory is always a part of lessons. I strongly believe that theory is needed so that students understand what they are playing and why.
To me, theory work is just as important as playing. A firm knowledge of musical structure makes playing everything easier.
Music knowledge learned through piano lessons transfers easily to other musical activities. Students in Fairfax County Public Schools, students learn to play recorder. Students are sometimes surprised to learn that they already know all the notes – from their piano lessons!
When you sing in a choir, harmonize with Sweet Adelines, play an instrument in your school or community band/orchestra, join your church’s handbell choir (note: Pender UMC has an excellent Handbell program), teach yourself guitar – theory will help in every instance. By learning to read, write, and understand this musical language, many more musical opportunities will be made available the rest of your life.
Most piano methods come with a theory book that matches page by page what concepts are being learned in the lesson books. I actually recommend that students do the theory first when they get home, while the concepts are still fresh in their minds.
If the student is not in a piano method, I’m starting to use the Theory Time series. Book One covers music alphabet, introduction to keyboard and staff, stem rule, steps & skips on a keyboard and staff, repeated notes, dynamics, treble clef lines & spaces, bass clef lines & spaces, quarter note & rest, half note & rest, whole note & rest, dotted half note, bar lines, double bar line, measures, time signatures, rhythm drill, vocabulary, ear training and a review test. Free ear training videos for each ear training exercise are hosted on the Theory Time YouTube channel. The Grade One workbook is appropriate for beginning 1st, 2nd or 3rd grade students. This workbook includes 51 pages, 13 lessons and 8 Fun Sheets.
For adults and more advanced students, I have a copy of All About Music Theory: A Fun and Simple Guide to Understanding Music which can be used as a review or a “try before buy”.
Stop procrastinating and go do your theory!



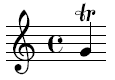
![A table depicting how to perform different types of trills when playing music from the Baroque period (1600-1750).[4] Note the similarity between the symbol for trill and that of the mordent.](https://oconnormusicstudio.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/03/baroque_trill_instructions.png?w=549&h=393)





